ABOUT US
- Profile
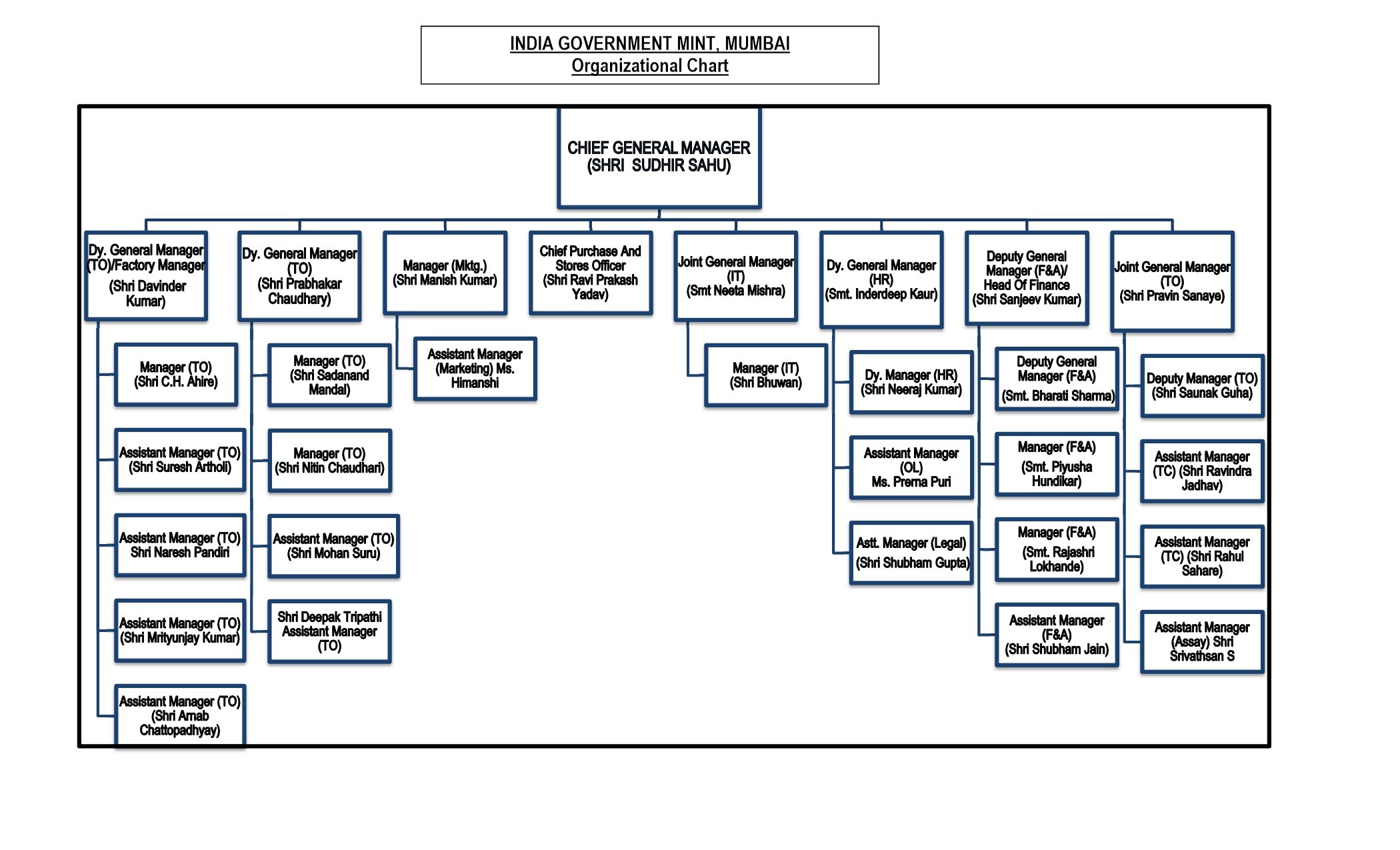
- Organization Structure
- History
Profile
India Government Mint, Mumbai (‘IGM Mumbai’), a unit of SPMCIL, is engaged in the manufacture of circulation coins, commemorative coins, medals and medallions, and weights & measures standards. In addition, the unit undertakes gold and silver refining activity and is also equipped with an Assay laboratory. The IGM Mumbai, established in 1829, is one of the oldest mint in India.
The unit offers comprehensive range of services covering every stage of minting process – from planning to finished products. Other products manufactured in the mint include verification stamps, identification stamps, quarter stamps, and obliterating stamps.
It is an NABL/ ISO: 17025:2017, 17034: 2016, 17043:2010, 9001:2015, 14001:2015, 45001:2018 certified institution.
History
Mumbai Mint is one of the oldest mints of India. The history of the Mumbai mint dates back to the last quarter of the seventeenth century. The first mint at Mumbai was set up by Governor Aungier for coinage of rupees, pies and bajruks. The first Mumbai Mint rupee was coined in the year 1672. These coins were minted in the Mumbai castle, now INS Angre near Town Hall.
Present Mumbai mint was constructed between the years 1824 and 1830 by Capt. John Hawkins of Bombay Engineers. Mr. James Farish was appointed as the master of mint from January 1830. For many years, 1.5 lakh coins were produced daily on three steam engines.
Mumbai mint was, then, under the administrative control of Government of Bombay. In 1876, Mumbai mint was transferred to the Government of India. A new branch of the Royal Mint of London was opened here during the year 1918-1919 with the objectives of coining the British sovereigns in India. After coining nearly 13 lakh sovereigns, this branch was closed in April 1919.
In 1919, Gold refinery was started in Mumbai Mint. It employed chlorine process for gold refining and refined raw gold from South Africa and Indian mines. Silver refinery was started in 1929 with an installed annual capacity of 80 million ounces of silver.
In 1964, Mint started producing commemorative coins. The first commemorative coin was in the memory of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru. Post 1958, Mumbai Mint started supplying Reference, Secondary and Working Standards sets after checking against accurate standards authenticated, calibrated and approved by NPL, New Delhi.
Mumbai Mint is one of the oldest mints of India. The history of the Mumbai mint dates back to the last quarter of the seventeenth century. It’s evolution over the centuries is identical to that of the rupee. The development of coins, from manufacturing the coins in a small place by means of hammer and anvil initially, to manufacturing by automatic machines, includes many interesting stories, for instance, in olden days the weight of the coins was decided in terms of grains.
The first mint at Mumbai was set up by Governor Aungier for the coinage of rupees, pies and bajruks. The first Mumbai Mint rupee was coined in the year 1672. These coins were minted in the Mumbai castle, now INS Angre near Town Hall. A water tank was located where now stands the multi-storied building of the Reserve Bank of India.
Present Mumbai mint was constructed between the years 1824 and 1830 by Capt. John Hawkins of Bombay Engineers. Mr. James Farish was appointed as the master of mint from January 1830. For many years 1,50,000 coins daily were produced on three steam engines in this mint.
In the year 1863 Col Ballard became the Master of Mumbai mint. He was the most famous British master of this mint. He reclaimed the land from the sea which is now known as Bellard Estate, the name given to perpetuate his memory.
Mumbai mint was, then, under the administrative control of government of Bombay. In 1876, Mumbai mint was transferred to the Government of India by Finance Department Resolution No 247, dated 18/05/1876. Till 1893, the operation of Indian mints was regulated by Coinage Acts of XVII 1835, XIII of 1862 and XXIII of 1870. Under the new Indian Coinage Act 1906, as amended from time to time a coin can be minted up to a denomination of rupees one thousand.
A new branch of the Royal Mint of London was opened here during the year 1918-1919 with the objectives of coining the British sovereigns in India. After coining 12.95 lakh sovereigns, this branch was closed in April 1919.Later it was converted in to the residence of the Mint Master. It is now known as the Mint House.
In 1919, Gold refinery was started in the Mumbai Mint. It employed the chlorine process for gold refining. It refined raw gold from South Africa and Indian mines. Silver refinery was started in 1929. It had an installed annual capacity of 80 million ounces of silver.
In 1964 production of commemorative coins was started. The first commemorative coin was in the memory of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru. Mumbai Mint has made a significant contribution in Indian coinage and gold refining.